Product Description
Product Description
SWC-I Series-Light-Duty Designs Cardan shaft
Designs
Type A — Welded shaft design,;with length compensation
Type B — Welded shaft design,;without length compensation
Type C — Short flanged design,;without length compensation
Data and Size of SWC-I Series Universal Joint Couplings
| Type | Desian Data Item |
SWC-I 58 |
SWC-I 65 |
SWC-I 75 |
SWC-I 90 |
SWC-I 100 |
SWC-I 120 |
SWC-I 150 |
SWC-I 180 |
SWC-I 200 |
SWC-I 225 |
| A | L | 255 | 285 | 335 | 385 | 445 | 500 | 590 | 640 | 775 | 860 |
| Lv | 35 | 40 | 40 | 45 | 55 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 100 | 120 | |
| m(kg); | 2.;2 | 3.;0 | 5.;0 | 6.;6 | 9.;5 | 17 | 32 | 40 | 76 | 128 | |
| B | L | 150 | 175 | 200 | 240 | 260 | 295 | 370 | 430 | 530 | 600 |
| m(kg); | 1.;7 | 2.;4 | 3.;8 | 5.;7 | 7.;7 | 13.;1 | 23 | 28 | 55 | 98 | |
| C | L | 128 | 156 | 180 | 208 | 220 | 252 | 340 | 348 | 440 | 480 |
| m(kg); | 1.;3 | 1.;95 | 3.;1 | 5.;0 | 7.;0 | 12.;3 | 22 | 30 | 56 | 96 | |
| Tn(N·m); | 150 | 200 | 400 | 750 | 1250 | 2500 | 4500 | 8400 | 16000 | 22000 | |
| Tf(N·m); | 75 | 100 | 200 | 375 | 630 | 1250 | 2250 | 4200 | 8000 | 11000 | |
| β(°); | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| D | 52 | 63 | 72 | 92 | 100 | 112 | 142 | 154 | 187 | 204 | |
| Df | 58 | 65 | 75 | 90 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 200 | 225 | |
| D1 | 47 | 52 | 62 | 74.;5 | 84 | 101.;5 | 130 | 155.;5 | 170 | 196 | |
| D2(H9); | 30 | 35 | 42 | 47 | 57 | 75 | 90 | 110 | 125 | 140 | |
| D3 | 38 | 38 | 4 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 89 | 102 | 114 | 140 | |
| Lm | 32 | 39 | 45 | 52 | 55 | 63 | 85 | 87 | 110 | 120 | |
| k | 3.;5 | 4.;5 | 5.;5 | 6.;0 | 8.;0 | 8.;0 | 10.;0 | 12.;0 | 14.;0 | 15.;0 | |
| t | 1.;5 | 1.;7 | 2.;0 | 2.;5 | 2.;5 | 2.;5 | 3.;0 | 4.;0 | 4.;0 | 5.;0 | |
| n | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| d | 5.;1 | 6.;5 | 6.;5 | 8.;5 | 8.;5 | 10.;5 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 17 | |
| MI(kg); | 0.;14 | 0.;16 | 0.;38 | 0.;38 | 0.;53 | 0.;53 | 0.;87 | 0.;87 | 1.;65 | 2.;14 | |
| Flange bolt | size | M5 | M6 | M6 | M8 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M16 |
| Tightening torque(N·m); | 7 | 13 | 13 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 110 | 180 | 270 | 270 |
1.; Notations:;
L=Standard length,; or compressed length for designs with length compensation;
LV=Length compensation;
M=Weight;
Tn=Nominal torque(Yield torque 50% over Tn);;
TF=Fatigue torque,; I.; E.; Permissible torque as determined according to the fatigue strength
Under reversing loads;
β=Maximum deflection angle;
MI=weight per 100mm tube
2.; Millimeters are used as measurement units except where noted;
3.; Please consult us for customizations regarding length,; length compensation and Flange connections.;
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Hollow Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Drive shaft type
The driveshaft transfers torque from the engine to the wheels and is responsible for the smooth running of the vehicle. Its design had to compensate for differences in length and angle. It must also ensure perfect synchronization between its joints. The drive shaft should be made of high-grade materials to achieve the best balance of stiffness and elasticity. There are three main types of drive shafts. These include: end yokes, tube yokes and tapered shafts.
tube yoke
Tube yokes are shaft assemblies that use metallic materials as the main structural component. The yoke includes a uniform, substantially uniform wall thickness, a first end and an axially extending second end. The first diameter of the drive shaft is greater than the second diameter, and the yoke further includes a pair of opposing lugs extending from the second end. These lugs have holes at the ends for attaching the axle to the vehicle.
By retrofitting the driveshaft tube end into a tube fork with seat. This valve seat transmits torque to the driveshaft tube. The fillet weld 28 enhances the torque transfer capability of the tube yoke. The yoke is usually made of aluminum alloy or metal material. It is also used to connect the drive shaft to the yoke. Various designs are possible.
The QU40866 tube yoke is used with an external snap ring type universal joint. It has a cup diameter of 1-3/16″ and an overall width of 4½”. U-bolt kits are another option. It has threaded legs and locks to help secure the yoke to the drive shaft. Some performance cars and off-road vehicles use U-bolts. Yokes must be machined to accept U-bolts, and U-bolt kits are often the preferred accessory.
The end yoke is the mechanical part that connects the drive shaft to the stub shaft. These yokes are usually designed for specific drivetrain components and can be customized to your needs. Pat’s drivetrain offers OEM replacement and custom flanged yokes.
If your tractor uses PTO components, the cross and bearing kit is the perfect tool to make the connection. Additionally, cross and bearing kits help you match the correct yoke to the shaft. When choosing a yoke, be sure to measure the outside diameter of the U-joint cap and the inside diameter of the yoke ears. After taking the measurements, consult the cross and bearing identification drawings to make sure they match.
While tube yokes are usually easy to replace, the best results come from a qualified machine shop. Dedicated driveshaft specialists can assemble and balance finished driveshafts. If you are unsure of a particular aspect, please refer to the TM3000 Driveshaft and Cardan Joint Service Manual for more information. You can also consult an excerpt from the TSB3510 manual for information on angle, vibration and runout.
The sliding fork is another important part of the drive shaft. It can bend over rough terrain, allowing the U-joint to keep spinning in tougher conditions. If the slip yoke fails, you will not be able to drive and will clang. You need to replace it as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous driving conditions. So if you notice any dings, be sure to check the yoke.
If you detect any vibrations, the drivetrain may need adjustment. It’s a simple process. First, rotate the driveshaft until you find the correct alignment between the tube yoke and the sliding yoke of the rear differential. If there is no noticeable vibration, you can wait for a while to resolve the problem. Keep in mind that it may be convenient to postpone repairs temporarily, but it may cause bigger problems later.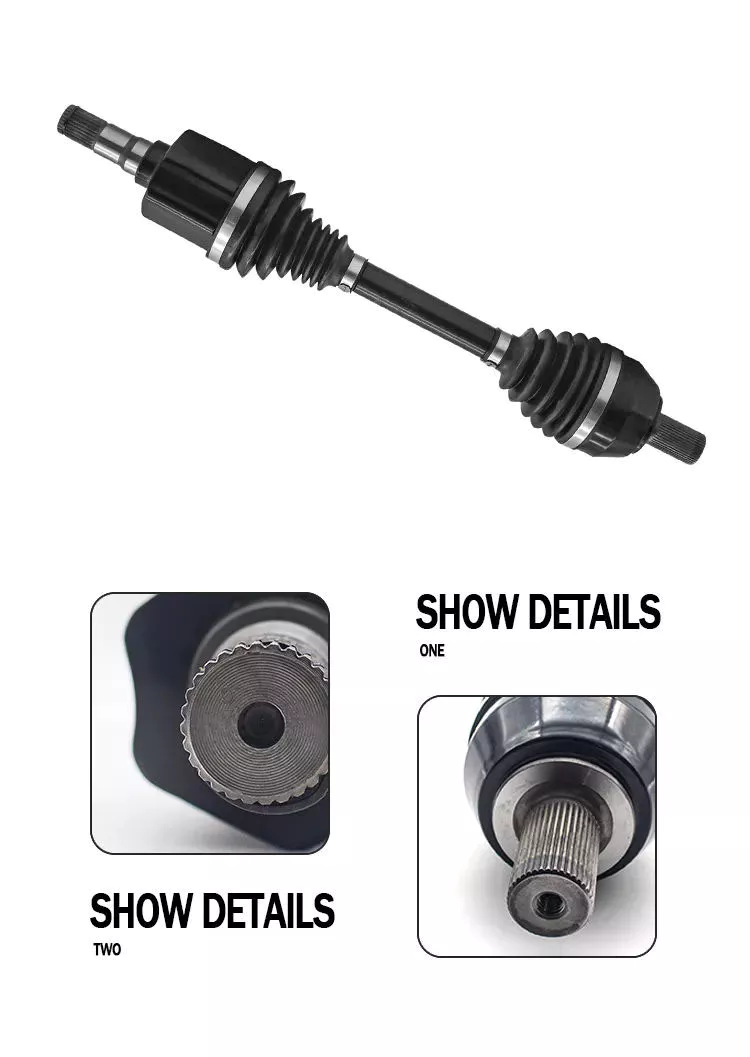
end yoke
If your driveshaft requires a new end yoke, CZPT has several drivetrain options. Our automotive end yoke inventory includes keyed and non-keyed options. If you need tapered or straight holes, we can also make them for you.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener that has U-shaped threads on its legs. They are often used to join two heads back to back. These are convenient options to help keep drivetrain components in place when driving over rough terrain, and are generally compatible with a variety of models. U-bolts require a specially machined yoke to accept them, so be sure to order the correct size.
The sliding fork helps transfer power from the transfer case to the driveshaft. They slide in and out of the transfer case, allowing the u-joint to rotate. Sliding yokes or “slips” can be purchased separately. Whether you need a new one or just a few components to upgrade your driveshaft, 4 CZPT Parts will have the parts you need to repair your vehicle.
The end yoke is a necessary part of the drive shaft. It connects the drive train and the mating flange. They are also used in auxiliary power equipment. CZPT’s drivetrains are stocked with a variety of flanged yokes for OEM applications and custom builds. You can also find flanged yokes for constant velocity joints in our extensive inventory. If you don’t want to modify your existing drivetrain, we can even make a custom yoke for you.


editor by CX 2023-06-13