Product Description
Product Description
SWC-I Series-Light-Duty Designs Cardan shaft
Designs
Type A — Welded shaft design,;with length compensation
Type B — Welded shaft design,;without length compensation
Type C — Short flanged design,;without length compensation
Data and Size of SWC-I Series Universal Joint Couplings
| Type | Desian Data Item |
SWC-I 58 |
SWC-I 65 |
SWC-I 75 |
SWC-I 90 |
SWC-I 100 |
SWC-I 120 |
SWC-I 150 |
SWC-I 180 |
SWC-I 200 |
SWC-I 225 |
| A | L | 255 | 285 | 335 | 385 | 445 | 500 | 590 | 640 | 775 | 860 |
| Lv | 35 | 40 | 40 | 45 | 55 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 100 | 120 | |
| m(kg); | 2.;2 | 3.;0 | 5.;0 | 6.;6 | 9.;5 | 17 | 32 | 40 | 76 | 128 | |
| B | L | 150 | 175 | 200 | 240 | 260 | 295 | 370 | 430 | 530 | 600 |
| m(kg); | 1.;7 | 2.;4 | 3.;8 | 5.;7 | 7.;7 | 13.;1 | 23 | 28 | 55 | 98 | |
| C | L | 128 | 156 | 180 | 208 | 220 | 252 | 340 | 348 | 440 | 480 |
| m(kg); | 1.;3 | 1.;95 | 3.;1 | 5.;0 | 7.;0 | 12.;3 | 22 | 30 | 56 | 96 | |
| Tn(N·m); | 150 | 200 | 400 | 750 | 1250 | 2500 | 4500 | 8400 | 16000 | 22000 | |
| Tf(N·m); | 75 | 100 | 200 | 375 | 630 | 1250 | 2250 | 4200 | 8000 | 11000 | |
| β(°); | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| D | 52 | 63 | 72 | 92 | 100 | 112 | 142 | 154 | 187 | 204 | |
| Df | 58 | 65 | 75 | 90 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 200 | 225 | |
| D1 | 47 | 52 | 62 | 74.;5 | 84 | 101.;5 | 130 | 155.;5 | 170 | 196 | |
| D2(H9); | 30 | 35 | 42 | 47 | 57 | 75 | 90 | 110 | 125 | 140 | |
| D3 | 38 | 38 | 4 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 89 | 102 | 114 | 140 | |
| Lm | 32 | 39 | 45 | 52 | 55 | 63 | 85 | 87 | 110 | 120 | |
| k | 3.;5 | 4.;5 | 5.;5 | 6.;0 | 8.;0 | 8.;0 | 10.;0 | 12.;0 | 14.;0 | 15.;0 | |
| t | 1.;5 | 1.;7 | 2.;0 | 2.;5 | 2.;5 | 2.;5 | 3.;0 | 4.;0 | 4.;0 | 5.;0 | |
| n | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| d | 5.;1 | 6.;5 | 6.;5 | 8.;5 | 8.;5 | 10.;5 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 17 | |
| MI(kg); | 0.;14 | 0.;16 | 0.;38 | 0.;38 | 0.;53 | 0.;53 | 0.;87 | 0.;87 | 1.;65 | 2.;14 | |
| Flange bolt | size | M5 | M6 | M6 | M8 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M16 |
| Tightening torque(N·m); | 7 | 13 | 13 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 110 | 180 | 270 | 270 |
1.; Notations:;
L=Standard length,; or compressed length for designs with length compensation;
LV=Length compensation;
M=Weight;
Tn=Nominal torque(Yield torque 50% over Tn);;
TF=Fatigue torque,; I.; E.; Permissible torque as determined according to the fatigue strength
Under reversing loads;
β=Maximum deflection angle;
MI=weight per 100mm tube
2.; Millimeters are used as measurement units except where noted;
3.; Please consult us for customizations regarding length,; length compensation and Flange connections.;
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Hollow Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
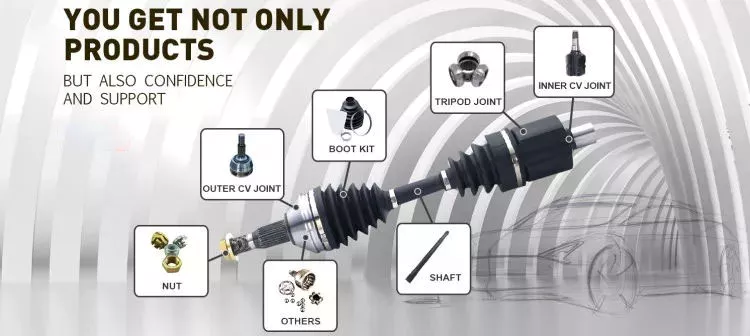
Drive shaft type
The driveshaft transfers torque from the engine to the wheels and is responsible for the smooth running of the vehicle. Its design had to compensate for differences in length and angle. It must also ensure perfect synchronization between its joints. The drive shaft should be made of high-grade materials to achieve the best balance of stiffness and elasticity. There are three main types of drive shafts. These include: end yokes, tube yokes and tapered shafts.
tube yoke
Tube yokes are shaft assemblies that use metallic materials as the main structural component. The yoke includes a uniform, substantially uniform wall thickness, a first end and an axially extending second end. The first diameter of the drive shaft is greater than the second diameter, and the yoke further includes a pair of opposing lugs extending from the second end. These lugs have holes at the ends for attaching the axle to the vehicle.
By retrofitting the driveshaft tube end into a tube fork with seat. This valve seat transmits torque to the driveshaft tube. The fillet weld 28 enhances the torque transfer capability of the tube yoke. The yoke is usually made of aluminum alloy or metal material. It is also used to connect the drive shaft to the yoke. Various designs are possible.
The QU40866 tube yoke is used with an external snap ring type universal joint. It has a cup diameter of 1-3/16″ and an overall width of 4½”. U-bolt kits are another option. It has threaded legs and locks to help secure the yoke to the drive shaft. Some performance cars and off-road vehicles use U-bolts. Yokes must be machined to accept U-bolts, and U-bolt kits are often the preferred accessory.
The end yoke is the mechanical part that connects the drive shaft to the stub shaft. These yokes are usually designed for specific drivetrain components and can be customized to your needs. Pat’s drivetrain offers OEM replacement and custom flanged yokes.
If your tractor uses PTO components, the cross and bearing kit is the perfect tool to make the connection. Additionally, cross and bearing kits help you match the correct yoke to the shaft. When choosing a yoke, be sure to measure the outside diameter of the U-joint cap and the inside diameter of the yoke ears. After taking the measurements, consult the cross and bearing identification drawings to make sure they match.
While tube yokes are usually easy to replace, the best results come from a qualified machine shop. Dedicated driveshaft specialists can assemble and balance finished driveshafts. If you are unsure of a particular aspect, please refer to the TM3000 Driveshaft and Cardan Joint Service Manual for more information. You can also consult an excerpt from the TSB3510 manual for information on angle, vibration and runout.
The sliding fork is another important part of the drive shaft. It can bend over rough terrain, allowing the U-joint to keep spinning in tougher conditions. If the slip yoke fails, you will not be able to drive and will clang. You need to replace it as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous driving conditions. So if you notice any dings, be sure to check the yoke.
If you detect any vibrations, the drivetrain may need adjustment. It’s a simple process. First, rotate the driveshaft until you find the correct alignment between the tube yoke and the sliding yoke of the rear differential. If there is no noticeable vibration, you can wait for a while to resolve the problem. Keep in mind that it may be convenient to postpone repairs temporarily, but it may cause bigger problems later.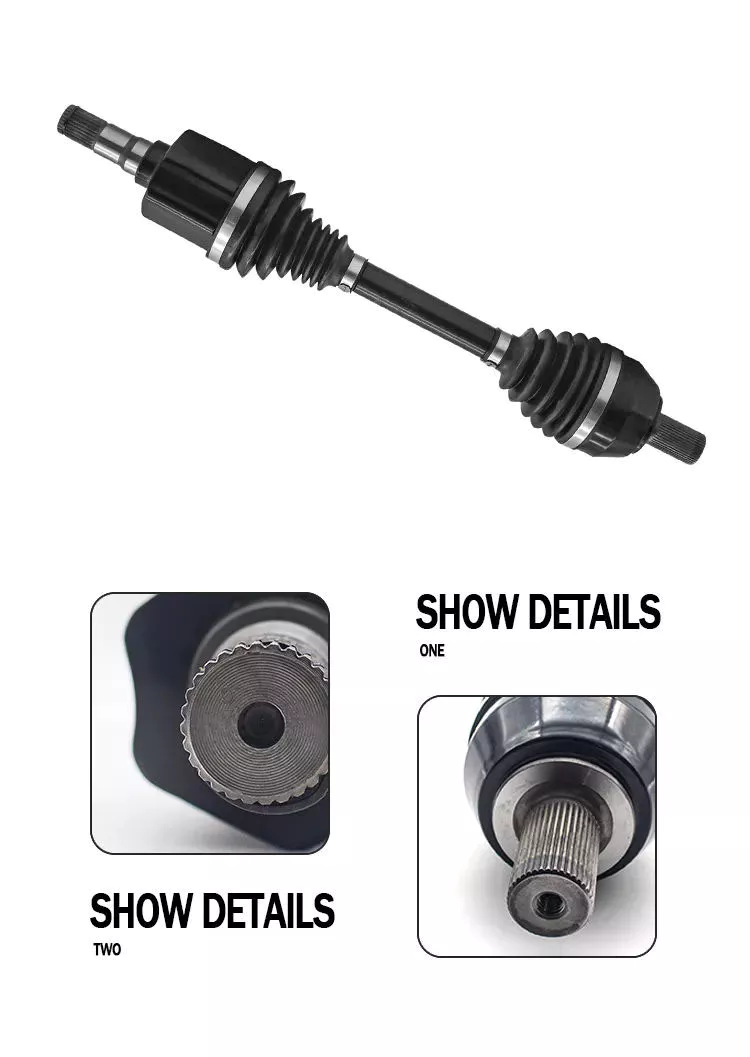
end yoke
If your driveshaft requires a new end yoke, CZPT has several drivetrain options. Our automotive end yoke inventory includes keyed and non-keyed options. If you need tapered or straight holes, we can also make them for you.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener that has U-shaped threads on its legs. They are often used to join two heads back to back. These are convenient options to help keep drivetrain components in place when driving over rough terrain, and are generally compatible with a variety of models. U-bolts require a specially machined yoke to accept them, so be sure to order the correct size.
The sliding fork helps transfer power from the transfer case to the driveshaft. They slide in and out of the transfer case, allowing the u-joint to rotate. Sliding yokes or “slips” can be purchased separately. Whether you need a new one or just a few components to upgrade your driveshaft, 4 CZPT Parts will have the parts you need to repair your vehicle.
The end yoke is a necessary part of the drive shaft. It connects the drive train and the mating flange. They are also used in auxiliary power equipment. CZPT’s drivetrains are stocked with a variety of flanged yokes for OEM applications and custom builds. You can also find flanged yokes for constant velocity joints in our extensive inventory. If you don’t want to modify your existing drivetrain, we can even make a custom yoke for you.


editor by CX 2023-06-13
China 1000w electric motorcycle&ATV for adult easy to drive electric motor LED Light Turn signal Two seat electric 4 wheel drive atv drive shaft equipment
Error:获取session失败,

Driveshaft structure and vibrations associated with it
The structure of the drive shaft is critical to its efficiency and reliability. Drive shafts typically contain claw couplings, rag joints and universal joints. Other drive shafts have prismatic or splined joints. Learn about the different types of drive shafts and how they work. If you want to know the vibrations associated with them, read on. But first, let’s define what a driveshaft is.
transmission shaft
As the demand on our vehicles continues to increase, so does the demand on our drive systems. Higher CO2 emission standards and stricter emission standards increase the stress on the drive system while improving comfort and shortening the turning radius. These and other negative effects can place significant stress and wear on components, which can lead to driveshaft failure and increase vehicle safety risks. Therefore, the drive shaft must be inspected and replaced regularly.
Depending on your model, you may only need to replace one driveshaft. However, the cost to replace both driveshafts ranges from $650 to $1850. Additionally, you may incur labor costs ranging from $140 to $250. The labor price will depend on your car model and its drivetrain type. In general, however, the cost of replacing a driveshaft ranges from $470 to $1850.
Regionally, the automotive driveshaft market can be divided into four major markets: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World. North America is expected to dominate the market, while Europe and Asia Pacific are expected to grow the fastest. Furthermore, the market is expected to grow at the highest rate in the future, driven by economic growth in the Asia Pacific region. Furthermore, most of the vehicles sold globally are produced in these regions.
The most important feature of the driveshaft is to transfer the power of the engine to useful work. Drive shafts are also known as propeller shafts and cardan shafts. In a vehicle, a propshaft transfers torque from the engine, transmission, and differential to the front or rear wheels, or both. Due to the complexity of driveshaft assemblies, they are critical to vehicle safety. In addition to transmitting torque from the engine, they must also compensate for deflection, angular changes and length changes.
type
Different types of drive shafts include helical shafts, gear shafts, worm shafts, planetary shafts and synchronous shafts. Radial protruding pins on the head provide a rotationally secure connection. At least one bearing has a groove extending along its circumferential length that allows the pin to pass through the bearing. There can also be two flanges on each end of the shaft. Depending on the application, the shaft can be installed in the most convenient location to function.
Propeller shafts are usually made of high-quality steel with high specific strength and modulus. However, they can also be made from advanced composite materials such as carbon fiber, Kevlar and fiberglass. Another type of propeller shaft is made of thermoplastic polyamide, which is stiff and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Both drive shafts and screw shafts are used to drive cars, ships and motorcycles.
Sliding and tubular yokes are common components of drive shafts. By design, their angles must be equal or intersect to provide the correct angle of operation. Unless the working angles are equal, the shaft vibrates twice per revolution, causing torsional vibrations. The best way to avoid this is to make sure the two yokes are properly aligned. Crucially, these components have the same working angle to ensure smooth power flow.
The type of drive shaft varies according to the type of motor. Some are geared, while others are non-geared. In some cases, the drive shaft is fixed and the motor can rotate and steer. Alternatively, a flexible shaft can be used to control the speed and direction of the drive. In some applications where linear power transmission is not possible, flexible shafts are a useful option. For example, flexible shafts can be used in portable devices.
put up
The construction of the drive shaft has many advantages over bare metal. A shaft that is flexible in multiple directions is easier to maintain than a shaft that is rigid in other directions. The shaft body and coupling flange can be made of different materials, and the flange can be made of a different material than the main shaft body. For example, the coupling flange can be made of steel. The main shaft body is preferably flared on at least one end, and the at least one coupling flange includes a first generally frustoconical projection extending into the flared end of the main shaft body.
The normal stiffness of fiber-based shafts is achieved by the orientation of parallel fibers along the length of the shaft. However, the bending stiffness of this shaft is reduced due to the change in fiber orientation. Since the fibers continue to travel in the same direction from the first end to the second end, the reinforcement that increases the torsional stiffness of the shaft is not affected. In contrast, a fiber-based shaft is also flexible because it uses ribs that are approximately 90 degrees from the centerline of the shaft.
In addition to the helical ribs, the drive shaft 100 may also contain reinforcing elements. These reinforcing elements maintain the structural integrity of the shaft. These reinforcing elements are called helical ribs. They have ribs on both the outer and inner surfaces. This is to prevent shaft breakage. These elements can also be shaped to be flexible enough to accommodate some of the forces generated by the drive. Shafts can be designed using these methods and made into worm-like drive shafts.
vibration
The most common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper installation. There are five common types of driveshaft vibration, each related to installation parameters. To prevent this from happening, you should understand what causes these vibrations and how to fix them. The most common types of vibration are listed below. This article describes some common drive shaft vibration solutions. It may also be beneficial to consider the advice of a professional vibration technician for drive shaft vibration control.
If you’re not sure if the problem is the driveshaft or the engine, try turning on the stereo. Thicker carpet kits can also mask vibrations. Nonetheless, you should contact an expert as soon as possible. If vibration persists after vibration-related repairs, the driveshaft needs to be replaced. If the driveshaft is still under warranty, you can repair it yourself.
CV joints are the most common cause of third-order driveshaft vibration. If they are binding or fail, they need to be replaced. Alternatively, your CV joints may just be misaligned. If it is loose, you can check the CV connector. Another common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper assembly. Improper alignment of the yokes on both ends of the shaft can cause them to vibrate.
Incorrect trim height can also cause driveshaft vibration. Correct trim height is necessary to prevent drive shaft wobble. Whether your vehicle is new or old, you can perform some basic fixes to minimize problems. One of these solutions involves balancing the drive shaft. First, use the hose clamps to attach the weights to it. Next, attach an ounce of weight to it and spin it. By doing this, you minimize the frequency of vibration.
cost
The global driveshaft market is expected to exceed (xxx) million USD by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of XX%. Its soaring growth can be attributed to several factors, including increasing urbanization and R&D investments by leading market players. The report also includes an in-depth analysis of key market trends and their impact on the industry. Additionally, the report provides a comprehensive regional analysis of the Driveshaft Market.
The cost of replacing the drive shaft depends on the type of repair required and the cause of the failure. Typical repair costs range from $300 to $750. Rear-wheel drive cars usually cost more. But front-wheel drive vehicles cost less than four-wheel drive vehicles. You may also choose to try repairing the driveshaft yourself. However, it is important to do your research and make sure you have the necessary tools and equipment to perform the job properly.
The report also covers the competitive landscape of the Drive Shafts market. It includes graphical representations, detailed statistics, management policies, and governance components. Additionally, it includes a detailed cost analysis. Additionally, the report presents views on the COVID-19 market and future trends. The report also provides valuable information to help you decide how to compete in your industry. When you buy a report like this, you are adding credibility to your work.
A quality driveshaft can improve your game by ensuring distance from the tee and improving responsiveness. The new material in the shaft construction is lighter, stronger and more responsive than ever before, so it is becoming a key part of the driver. And there are a variety of options to suit any budget. The main factor to consider when buying a shaft is its quality. However, it’s important to note that quality doesn’t come cheap and you should always choose an axle based on what your budget can handle.


editor by Cx 2023-04-26